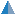
Creating or Modifying a Field from GUI
To add a field/column to a database table in Database Tour application, open the needed table, switch to the Fields page of the Table window, and click Add Field button.
To modify an existing field, click Edit Field button there or double-click any field attribute (except the name and number) in the corresponding row in the list of fields. Note: If Edit Field button is inactive or invisible, such a function is not supported for this table or database type.
Different database types have different set of field attributes. Even different versions of the same RDBMS might have different set of field attributes. Compare the interface of adding or modifying a field for Microsoft Access (left) and PostgreSQL v.17 (right) databases:
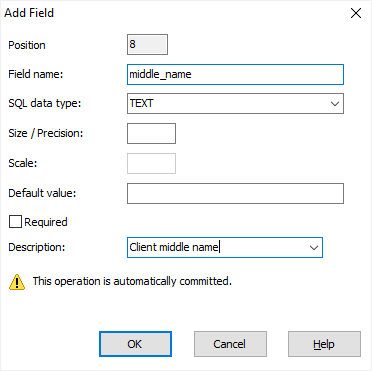
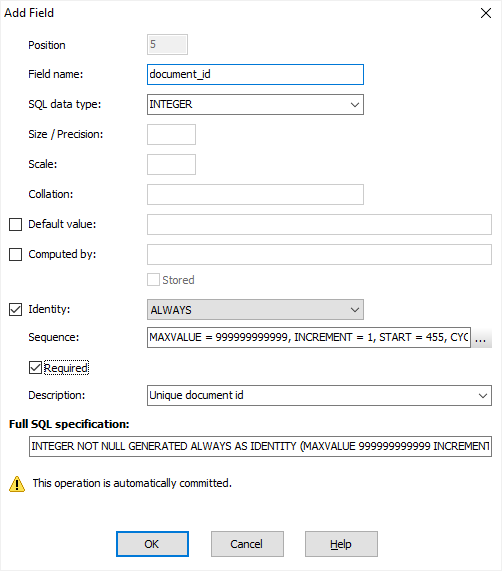
Before the table changes are applied to the database, you can check SQL commands generated for these changes. If everything is OK, click Execute. If you need to add or modify something, click Copy to Editor and continue with SQL code in a new SQL window. Otherwise, click Cancel.
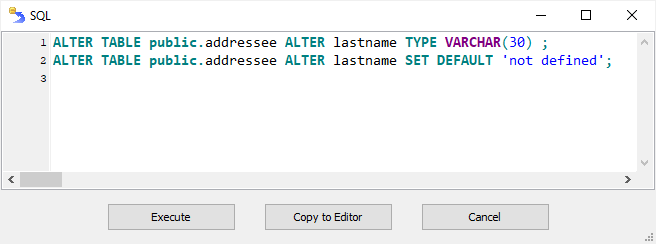
Creating or Modifying Field Options
| Field name | Specify a name for the field (when adding the field). |
| Data type | Specify the data type for the field (if your database is not SQL-based database). |
| SQL data type | Specify the SQL data type for the field (if your database is SQL-based database). |
| Size / Precision | Specify the field size (for text compatible and some other field types like BLOB etc.) or field precision (for numeric fields). |
| Scale | Specify the field scale for fields to hold floating-point numbers. This is the number of digits allowed after the decimal point. |
| Character set | Specify the character set (for text fields). Supported for: MySQL, Interbase, Firebird. |
| Collation | Specify the collation (for text fields). Supported for: SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Interbase, Firebird. |
| Default value | Specify default value for the field. |
| Computed by | Specify a formula for computed fields. Supported for: SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Interbase, Firebird. |
| Stored | Specify whether to store the result of the calculation for computed fields in the database. Supported for: SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL. |
| Identity | Specify the type of identity/auto-increment field (integer and compatible). Supported for: SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Firebird. |
| Sequence | Specify the sequence parameters for identity/auto-increment field. Supported for: SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Firebird. |
| Required | Specify whether the field is required (i.e. does not allow NULL values). |
| Description | Specify the field description. Supported for: SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL. |
Creating or Modifying a Field by SQL
Alternatively, you can create or modify fields by SQL means (except a few types of databases which does not support this).
For example, the next SQL command adds a new text field to a table (check the correct syntax for your database):
ALTER TABLE clients ADD middle_name VARCHAR (30)This command sets the default value for a column in Firebird database:
ALTER TABLE clients ALTER COLUMN added SET DEFAULT current_dateAnd this command changes the column type in PostgreSQL database:
ALTER TABLE clients ALTER COLUMN middle_name TYPE TEXTIn some databases, you should type and execute a separate command to add a column comment (if you need this and the database supports this).
Please read your database documentation to learn the correct syntax and possible options.
See also