Use this format to export data to Microsoft Excel workbook (as XML). The export process is performed by Database Tour export engine with direct file access and therefore is very fast.
The data can be exported to Excel (XML-based) format either from Database Tour (Pro) GUI or from the Database Tour Pro command line.
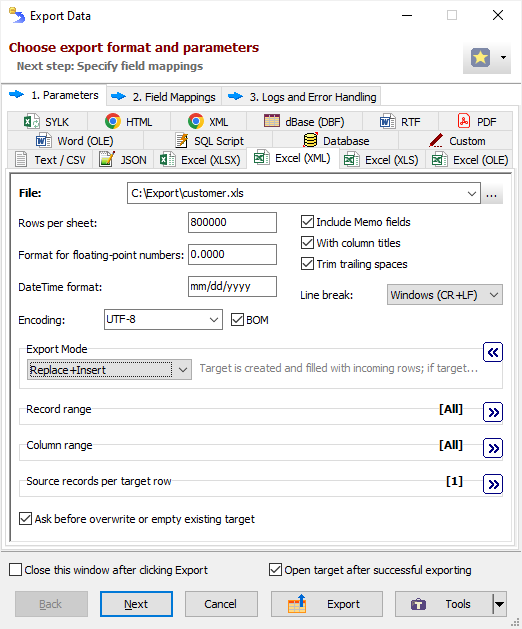
When exporting data from GUI, switch to Excel (XML) page of the Export dialog. If this page is not visible, click Favorite Export Formats button in the top-right corner of the window and make sure the corresponding format is selected.
Format Specific Options
File - when exporting data from a table or SQL query, or when exporting data from a group of tables (multi-table export), specify a file name to export data to. In case of multi-table exporting, all tables will be outputted to one target file, each table on a separate Excel sheet. The option is not available when exporting data to clipboard.
Folder - when exporting data from a group of tables (multi-table export), specify a folder name to export data to. Each table will be exported to a separate file in the specified folder; file names can be specified in Table Mappings. The option is not available when exporting data to clipboard.
Table title - specify the table title, i.e. text which is shown above the table data in the target document. Available when exporting data to one file; for multi-table exporting, table titles can be specified at the Table Mappings step. Can be blank. Command line equivalent: /TableTitle.
Rows per sheet - specify how many rows should contain an Excel sheet. If the number of passed rows in exporting procedure reaches this value, a new sheet is automatically created and the data output is continued into the new sheet. Command line equivalent: /RowsPerSheet.
Floating-point numbers format - specify format for floating-point numbers. For example, 0.00. Command line equivalent: /FloatFormat.
DateTime format - specify format for DateTime values. For example, mm/dd/yyyy. Command line equivalent: /DateTimeFormat.
Encoding - specify XML encoding. Command line equivalent: /Encoding.
BOM - specify whether to include BOM (byte order mark) when using Unicode encoding. Reverse command line equivalent: /NoBom.
Append timestamp to file - specify whether to append current timestamp to the end of the target file name. The timestamp mask is _YYYYMMDD_HH24MISS. Command line equivalent: /AppendTimestamp.
Include MEMO fields - specify either to include contents of MEMO / CLOB fields in target or not; in the latter case, a constant describing the field type will be used instead of the field contents. Command line equivalent: /IncludeMemo.
Include column names - specify whether to include the column headers in the target. Command line equivalent: /IncludeColNames.
Trim trailing spaces - specify either to trim trailing spaces and control characters in target or not. Applicable for char and varchar data only. Using this option allows to remove useless data and thus reduce the output volume, and sometimes improve the target look. Command line equivalent: /TrimTrailingSpaces.
Line break - specify line break style; if you choose Windows, then each line in the file will be terminated by carriage return and new line character (CR+LF); if you choose Mac, a carriage return (CR) will be used to separate lines; otherwise, Unix style will be used (LF). Command line equivalent: /LineTerminator.
Export mode
Specify export mode:
|
REPLACE+INSERT Target file is created and filled with incoming rows; if the target file already exists, it is overwritten. |
|
CREATE_OR_REPLACE Blank target file (using appropriate structure) is created; if the target file already exists, it is overwritten. |
Note: For multi-table exporting, the value can be overridden for each individual table-to-file pair in Table mappings section.
Command line equivalent: /ExportMode.
Record range
Specify range of source records to be exported:
- Full table - all records are exported.
- Selected records only - only selected records are exported. To select rows, click the corresponding button and then select needed rows using Shift, Ctrl and arrow keys.
- From current record to the last one - all data between current and the last records are exported.
Limit the record count to - specify a maximum number of records to be exported. If this option is not specified or it is less then 1, all records from the specified record range will be exported. If you just want to create a file without data exporting, use the corresponding Export mode instead. Command line equivalent: /LimitRecordCount.
Column range
Specify range of source columns to be exported:
- All columns - all columns (including columns, which were temporary hidden by user) are exported.
- Selected column only - only selected (current) column is exported.
- Visible columns - only visible columns are exported.
Source records per target row
Specify a number of records from source database to be placed into one line of the target file. For example, if you specify 2, the source data will be placed to the target in the following way:
| Source | Target | |||||
| Col1 | Col2 | Col1 | Col2 | Col1 | Col2 | |
| cell1 | cell2 | >> | cell1 | cell2 | cell3 | cell4 |
| cell3 | cell4 | cell5 | cell6 | cell7 | cell8 | |
| cell5 | cell6 | |||||
| cell7 | cell8 | |||||
This option is useful when source have a small count of columns and a large count of rows. Using it, you can fill target area more optimally.
Command line equivalent: /RecordsPerLine.
Other options
Ask before overwrite or empty existing target - specify either to ask the user to overwrite existing target for REPLACE+INSERT and CREATE_OR_REPLACE export modes. The option is not available when exporting data to clipboard. Reverse command line equivalent: /SuppressOverwriteOrDeletePrompt.
See also